

2015 May 28(7):793-8.Ĭlark SL, Hankins GD, Dudley DA, Dildy GA, Porter TF. Amniotic fluid embolism: antepartum, intrapartum and demographic factors. Other causes of hemodynamic instability should be ruled out.Ĭopyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.įong A, Chau CT, Pan D, Ogunyemi DA. The diagnosis is of exclusion based on clinical presentation.
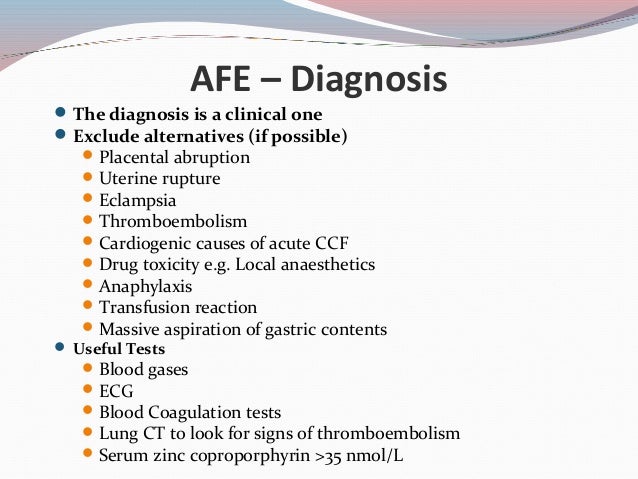
The diagnosis of AFE has been established at autopsy when fetal squamous cells are found in the maternal pulmonary artery blood however, fetal squamous cells are also sometimes present in the circulation of laboring women who do not develop AFE. Data from the National Amniotic Fluid Embolism Registry suggests that the process resembles anaphylaxis more than embolism, and the terminology of "anaphylactoid syndrome of pregnancy" has been recommended because fetal tissue or amniotic fluid components are not always found in women who present with signs and symptoms attributable to amniotic fluid embolism. Steiner and Luschbaugh first described amniotic fluid embolism in 1941, after they found fetal cells in the maternal pulmonary circulation, who died during labor. In the United States, AFE occurs in 2 to 8 per 100,000 deliveries and is the cause of maternal mortality between 7.5% to 10%. Survivors are frequently left with serious cardiac, renal, neurologic, and pulmonary dysfunction. The presentation is abrupt, usually with sudden cardiorespiratory collapse followed by severe coagulopathy and refractory resuscitation.

Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) represents the second leading cause of peripartum maternal death in the United States and the number one cause of peripartum cardiac arrest. Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a life-threatening obstetric emergency characterized by sudden cardiorespiratory collapse and disseminated intravascular coagulation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
